Solar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles, consisting mainly of electrons and protons, but also to a lesser extent helium (1-3%) and trace amounts of heavier ions.
The solar wind escapes from the solar corona (the highest layer of the Sun’s atmosphere) due to the pressure difference between the corona and interplanetary space. Every second, the Sun releases approximately 1.2 billion tonnes of solar wind mass.
The solar wind’s journey from the Sun to Earth usually takes between 2.5 and 6 days, depending on its speed. Based on the speed of the flow, the solar wind is divided into:
- fast – it reaches speeds of up to 800 km/s and originates mostly from so-called coronal holes in the polar regions of the Sun,
- slow – it flows at around 400 km/s and typically escapes from the equatorial regions of the Sun. This type of solar wind affects the planets of the Solar System, including Earth

In the vicinity of the Earth, the density of solar wind particles is around 3-20 particles per cm³. Although the solar wind is very sparse, when it collides with the Earth’s magnetosphere it can cause geomagnetic storms and affect the functioning of satellites, telecommunication networks or electricity grids. The solar wind electrons that penetrate the upper atmosphere in the Earth’s polar regions then transfer their energy to atoms and air molecules. These excited particles subsequently emit light, creating the auroras typical of the Nordic regions [1], [2].
For these reasons, it is important to monitor, measure and record the characteristics of the solar wind. Space probes are used for this purpose. They must be able to record solar wind parameters with high temporal resolution and accuracy. The probes are thus equipped with sophisticated instruments, which include so-called Faraday Cylinders (FC). One such device (BMSW) contains up to 6 FCs [3].
Faraday cylinder
FC is a metallic element whose purpose is to capture and measure the flow of charged particles. It is used in both laboratory conditions and in space research to monitor not only the solar wind, but also the intensity of electron or ion beams and other energetic particles in space. For example, one of these devices has been placed on board the Spectr-R spacecraft.
The FC design includes several elements – a collector and a set of four grids. The collector collects charged particles. The outer and inner grids serve to shield the interfering external electric field so that the measurement is not affected by environmental influences. Between these grids is a so-called control grid, which is connected to a high-voltage power supply. This grid acts as an energy filter – only particles with sufficient kinetic energy overcome its potential and reach the collector. The fourth grid is the so-called suppressor grid, which is powered by a negative voltage. Its function is to deflect electrons from the solar wind, secondary electrons released from the other grids and photoelectrons that are produced on the collector by the sun’s ultraviolet radiation.
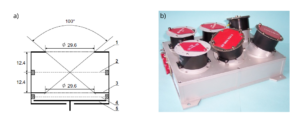
Fig. 1 a) Schematic of FC: (1) and (3) outer and inner grids, (2) control grid, (4) suppressor grid, (5) collector
b) BMSW solar wind monitoring instrument [3]
Production of Faraday cylinders: cooperation with MFF UK
In cooperation with the Faculty of Mathematics and Physics of Charles University, we participated in the production and preparation of grids for installation in the FC.
Blackening technology in FC component processing
Blackening is a technology based on the chemical treatment of the surface of metals in which a thin layer of black oxides is purposely formed on the parts. The layer becomes an integral part of the base material rather than an after-applied coating, as in physical vapour deposition (PVD) or electroplating technologies, for example. Blackening in our system significantly reduces reflectivity and gives metal components a deep matte black appearance. In addition, the blackening system used produces electrically conductive layers, which is an essential feature in the case of FC.
The black and deep matte appearance of the grids reduces the appearance of parasitic reflections and scattered radiation inside the measuring system, which contributes to increased accuracy and stability of the measurement. This reduces the risk of distortion of the measured data. In addition, the blackening process does not practically change the dimensions of the gratings and does not disturb the accuracy of the geometry produced, which is essential for the correct functioning of the gratings.
The basic material for the blackened grilles and other FC components are aluminium alloys and stainless steels. The careful reader may well ask why not, for example, anodise aluminium alloys black? The answer is simple… The black anodized layers are formed by discoloured Al2O3 oxides, which are electrically non-conductive and thus would not be able to form electrostatically and optically functional surfaces in the case of FC.
Because the “golden” rule that we can always choose the right technology only after we understand the purpose and all the requirements of the part and its surface treatment applies here as well.
Our optically deep matte black surfaces are therefore indispensable both in the field of FC implementation and, for example, in the field of light optics – see our article on slotted apertures.

Fig. 2 Blackened grids before installation in FC

Fig. 3 FC assembly
Sources
[1] P. Kulhánek, “Solar Wind,” Aldebaran Bulletin, no. 19, 2. May 2008. [Online]. Available: https://www.aldebaran.cz/bulletin/2008_19_swi.php.
[2] “Solar wind,” Observations of the Sun, [Online]. Available: https://pozorovanislunce.eu/vykladovy-slovnicek/slunecni-vitr.html.
[3] J. Vaverka, Z. Němeček, L. Přech, J. Šafránková, and A. Komárek, “Calibration of Faraday Cups used on the Spectr-R Spacecraft for Monitoring the Solar Wind,” WDS’11 Proceedings of Contributed Papers: Part II – Physics of Plasmas and Ionized Media, no. 2, pp. 34-39, 2011.
Don’t forget to follow us on our social networks. You can find us on facebook, instagram and linkedin.
Electroforming s.r.o. – We meet individual requirements from development to production.
